Introduction to LINQ Queries - C#
LINQ (Language Integrated Query) is a feature introduced in Visual Studio 2008 used for querying and updating data. It can be used with databases (LINQ to SqL, LINQ to Dataset, LINQ to Entities), XML (LINQ to Xml), and with Objects (LINQ to Objects).
1. Obtain the datasource.
2. Create the query.
3. Execute the query.
This is an example explaining these three operations:
1. Using Query Syntax :
This is the recommended way of writing the query syntax to create a query expression like the above example.
It consists of expressing the query as a method call. These methods must be called last in any query because they return a single value. The following example shows a method call in query expression:
3. Mixed Query and Method Synatx:
The following example explains this way
LINQ Tutorial
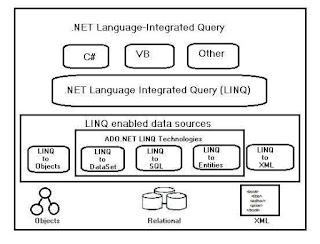
LINQ architecture in .NET:
LINQ has a 3 layered architecture, the upper layer consists of the languages extensions and the bottom layer consists of datasources that are IEnumerable or IQueryable. This architecture is figured in the image below:Example of LINQ Query in C#:
There are three operations in a LINQ query:1. Obtain the datasource.
2. Create the query.
3. Execute the query.
This is an example explaining these three operations:
class Test
{
static void Main()
{
// 1. Obtain data source.
string[] towns = new string[4] { "Algeria", "Tunisia", "Egypt", "Morocco"};
// 2. Query creation.
var townQuery =
from x in towns
where x.Length < 7
select x;
// 3. Query execution.
foreach (string s in townQuery)
{
Console.WriteLine(s);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
How to write LINQ Query in C#:
There are three ways in which we can write LINQ query in C#:1. Using Query Syntax :
This is the recommended way of writing the query syntax to create a query expression like the above example.
2. Using Method Syntax:It consists of expressing the query as a method call. These methods must be called last in any query because they return a single value. The following example shows a method call in query expression:
List<int> numbers1 = new List<int>() { 5, 4, 1, 3, 9, 8, 6, 7, 2, 0 };
List<int> numbers2 = new List<int>() { 15, 14, 11, 13, 19, 18, 16, 17, 12, 10 };
double average = numbers1.Average();
IEnumerable<int> concatenationQuery = numbers1.Concat(numbers2);
3. Mixed Query and Method Synatx:
The following example explains this way
int numCount1 =
(from num in numbers1
where num < 3 || num > 7
select num).Count();
IEnumerable<int> numbersQuery =
from num in numbers1
where num < 3 || num > 7
select num;
int numCount2 = numbersQuery.Count();
For more explanation check out this video:
References:
Ecrire des requêtes LINQ en C#LINQ Tutorial
Introduction to LINQ Queries - C#
 Reviewed by Bloggeur DZ
on
02:30
Rating:
Reviewed by Bloggeur DZ
on
02:30
Rating:
 Reviewed by Bloggeur DZ
on
02:30
Rating:
Reviewed by Bloggeur DZ
on
02:30
Rating:



Aucun commentaire: