Lambda expressions in C#
In the past article, we explained how to use Delegates with C#. However, as we have seen, the syntax of the delegates is a little bit hard. That's why the .Net Framework 3.0 propose the Lambda expressions.
Left side: Input parameters, it can be empty sometimes.
Right side: The statements list or the block instructions.
The following is an example of Lambda expression:
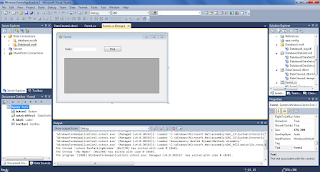
The example is developed with Visual Studio 2010, first we create the following Windows Form and of course we add Linq To Sql class to the project.
In findButton click event we add this code to populate the datagridview:
For example we use Lambda with Delegate:
The following example shows how to use Lambda expressions with Func:
http://www.dotnetdojo.com/guide-expressions-lambda-csharp/
Definition of Lambda expressions:
Lambda expression is an anonymous function containing expressions and functions. It may be used to create delegates or expression tree.Syntax of Lambda expressions:
(input parameters) => expression or statement block
Left side: Input parameters, it can be empty sometimes.
Right side: The statements list or the block instructions.
The following is an example of Lambda expression:
num => num + 10
Using Lambda expressions with LINQ:
The following example explains how to use Lambda expressions with Linq To Sql in C#.The example is developed with Visual Studio 2010, first we create the following Windows Form and of course we add Linq To Sql class to the project.
In findButton click event we add this code to populate the datagridview:
private void findButton_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
DataClasses1DataContext dc=new DataClasses1DataContext(con);
//using lambda expression with linq
var query = dc.Employees
.Where(emp => emp.Code == textBox1.Text)
.Select(emp => emp);
dataGridView1.DataSource = query.ToList();
}
Lambda statements:
Lambda statement is an expression Lambda which the statements (the right side) are enclosed in braces as follows:(input parameters) => {statement;}
For example we use Lambda with Delegate:
delegate void MyDelegate(string s);
…
MyDelegate myDel = n => { string s = n + " " + "World"; Console.WriteLine(s); };
myDel("Hello");
Lambda with the standard query operators:
The .Net Framework propose many methods that use Lambda expressions such Func<T,TResult> delegate type which is a delegate with parameters that defines type of parameters and the type of return delegate. This delegate is defined like:public delegate TResult Func(TArg0 arg0)
The following example shows how to use Lambda expressions with Func:
public void Main()
{
Func<int,int> myDelegate = x => x*x;
int square = myDelegate(5);
}
Conclusion:
Lambda expressions are now very used in .Net Framework, and these some points to remember while using:- A lambda expression can return a value and may have parameters.
- Parameters can be defined in a myriad of ways with a lambda expression.
- If there is single statement in a lambda expression, there is no need of curly brackets whereas if there are multiple statements, curly brackets as well as return value are essential to write.
- With lambda expressions, it is possible to access variables present outside of the lambda expression block by a feature known as closure. Use of closure should be done cautiously to avoid any problem.
- It is impossible to execute any unsafe code inside any lambda expression.
- Lambda expressions are not meant to be used on the operator’s left side.
References:
http://www.tutorialspoint.com/linq/linq_lambda_expressions.htmhttp://www.dotnetdojo.com/guide-expressions-lambda-csharp/
Lambda expressions in C#
 Reviewed by Bloggeur DZ
on
12:30
Rating:
Reviewed by Bloggeur DZ
on
12:30
Rating:
 Reviewed by Bloggeur DZ
on
12:30
Rating:
Reviewed by Bloggeur DZ
on
12:30
Rating:



Aucun commentaire: